Kraków 2020-03-26
00124a Section 1924
CWL Mokotów, WWS „Samolot” Hanriot H-28
Poland
School and sanitary aircraft
Historia



After the end of the Great World War in Poland, mainly three planes were used for training: Caudron G-3 from 1919, Nieuport 23m from 1918 and Albatros B-II from 1918. In 1923, it was decided to start serial production of a new school aircraft. In the absence of Polish constructions and extensive cooperation with France, it was decided to buy the Hanriot HD-14 aircraft.
The Hanriot HD-14 aircraft is a two-seater, biplane, powered by the Le Rhône C rotary engine, with 59 kW (80 HP). The first flight was made in 1923. Production in France began in 1924. Hanriot H (HD) -17 is a seaplane on floats.
In Poland, initially the production of Hanriot HD-14 aircraft was placed in the Central Aviation Workshops in Mokotów. In Warsaw, 75 copies were made of components supplied from France. The first plane was flown in December 1924.
There was also a proposal to build aircraft in Lublin. Eventually, the production of Hanriot aircraft was placed at Wielkopolska Wytwórnia Planów (WWS) "Airplane" in Poznań. WWS "Airplane" factory received the order in 1924. Semi-finished products from France were used to build the aircraft. The organization of production was also modeled on French methods.
On 1925-02-22, the first Hanriot HD-14 aircraft built in Poznań was baptized by General Włodzimierz Zagórski, responsible for the development of Polish Aviation. The aircraft made its first flight two days earlier, on 1925-02-20.
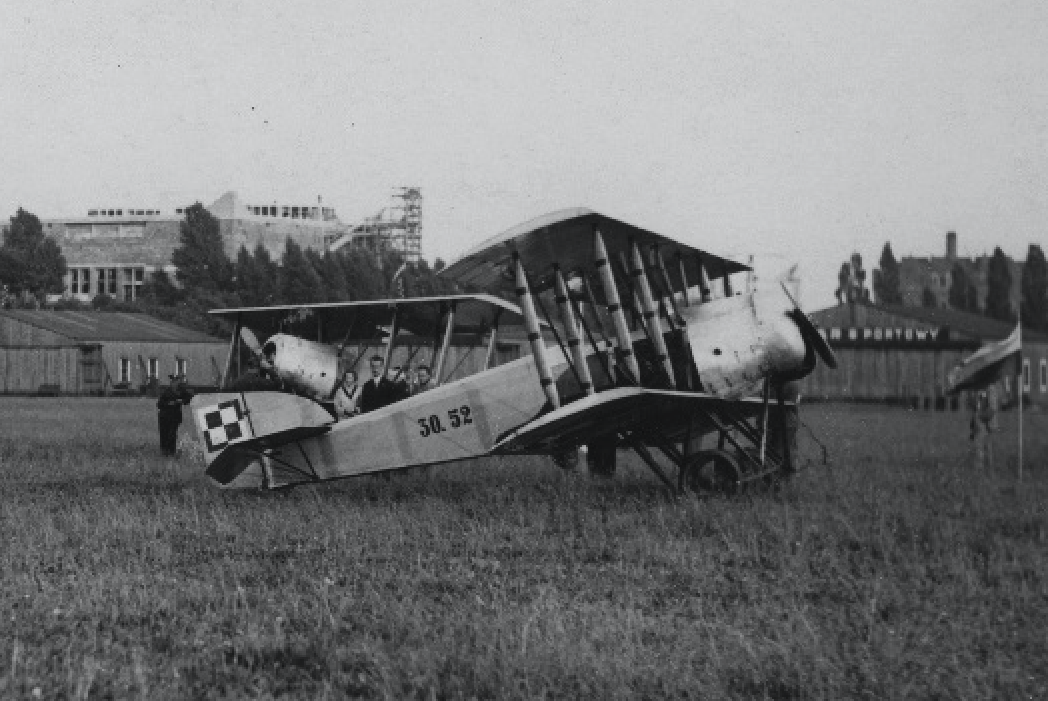
In the period 1925-1926, WWS "Airplane" built 120 machines, which were initially designated HD-14, and a little later Hanriot H-28. The Hanriot H-28 aircraft was called "Butterfly".
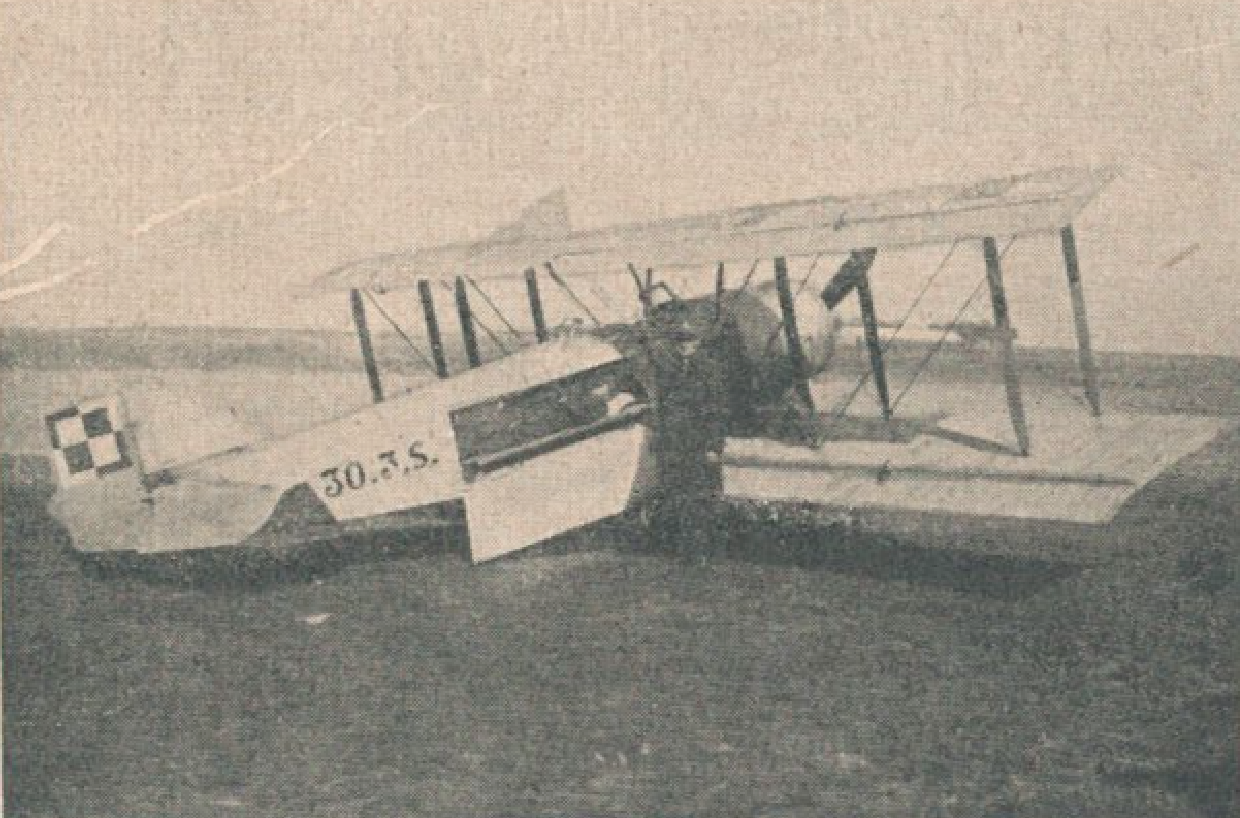
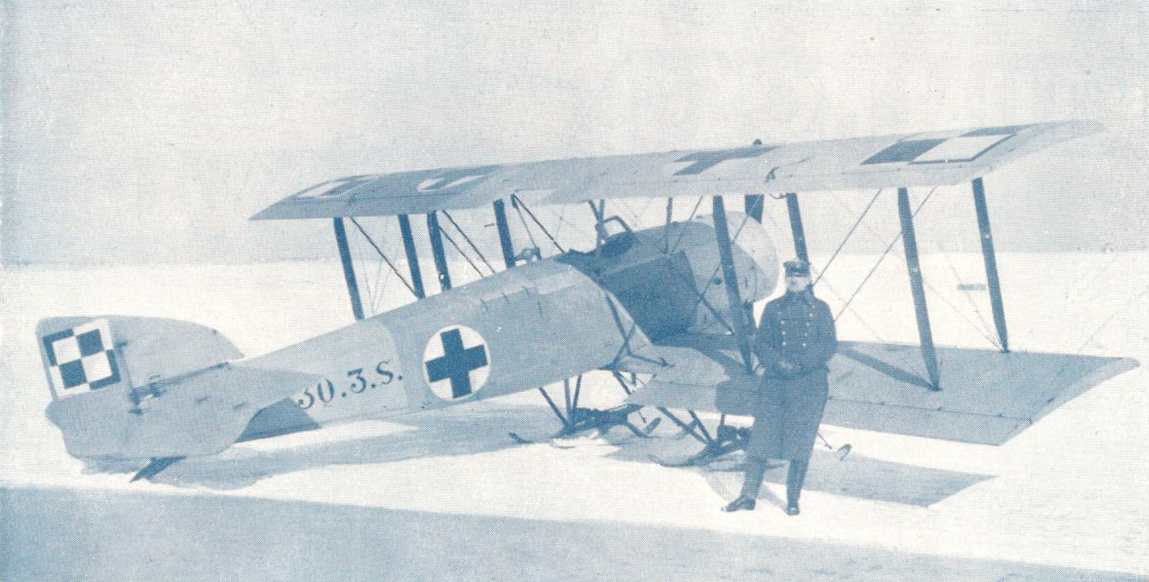
WWS Design Office "Airplane", based on Hanriot H-28, developed a sanitary version designed to transport one wounded on a stretcher. The aircraft received the designation H-28 S. In 1925, two aircraft were built, which were delivered in September and October 1925. The aircraft received the numbers 30.1 S and 30.2 S. In 1927-1928, 16 H-28 S were built. WW-H aircraft manufactured in WWS received the numerical type designation: 30 (numbers 30.3 S to 30.18 S).
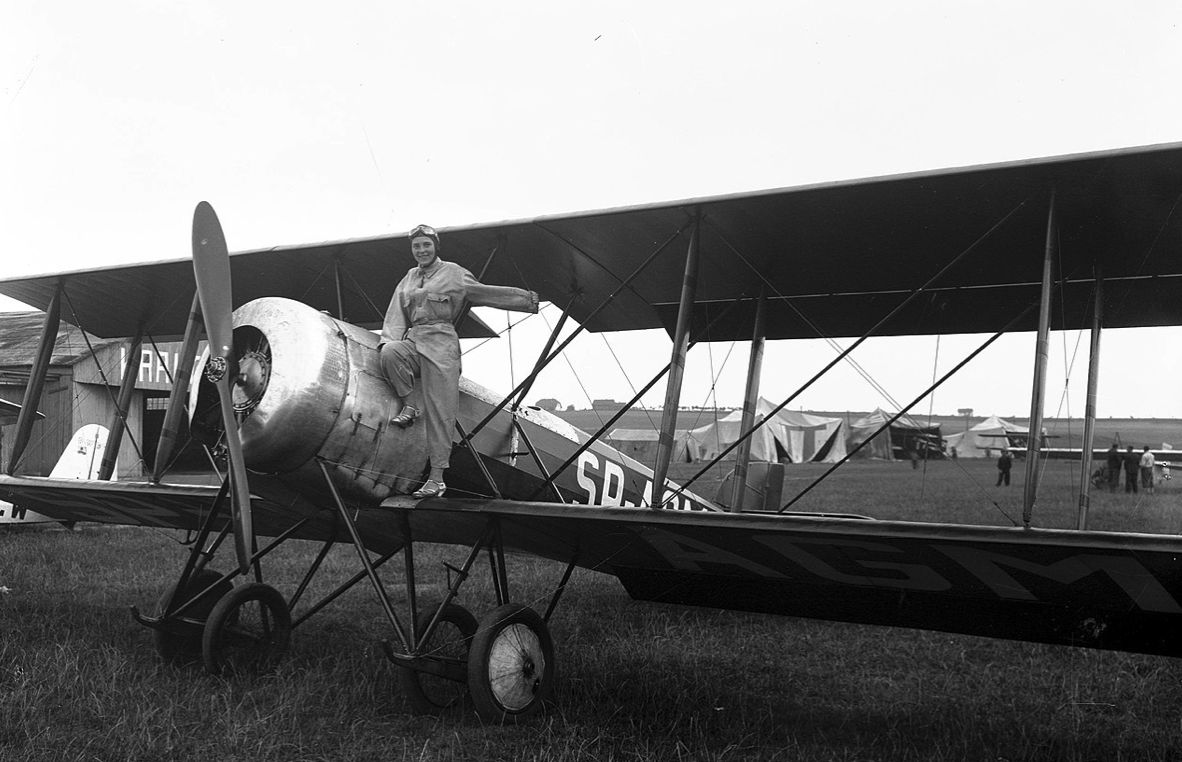
80 Hanriot H-19 aircraft were also built. it was an H-14 aircraft with a different engine. In total, around 200 aircraft were built. The Polish Army from France received 70 more aircraft. In total, there were 295 Hanriot H-28 and derivative aircraft in Poland. In addition to training, they were used to tow gliders and shooting sleeves. In the Polish Army, aircraft were used as liaison machines. In Warsaw, one aircraft received Rudlicki type tail. Eventually, Hanriot H-28 aircraft were withdrawn at the end of 1935, handing over the last machines to civil aviation: Aeroclubs, LOPP and Civilian Pilot School at the Poznań-Ławica airport.
Written by Karol Placha Hetman
Kraków 2020-03-26
00124a Section 1924
CWL Mokotów, WWS „Samolot” Hanriot H-28
Poland
School and sanitary aircraft
Construction
Two-seat biplane with wooden structure.
Wings
Double-girder wings of equal span and chord were of the same design, giving the possibility of exchange between them. Upper lobe, three-fold with canopy, lower two-fold. The wings are stiffened with posts and lashings. Cover made of canvas. The shuttlecocks are on both lobes.
Fuselage
Wooden hull with a truss structure, profiled with slats, stiffened, with wire strings inside. The engine cover and the front part are covered with aluminum sheet, the further cover is made of canvas. A 94 dm3 fuel tank was placed in the hull and a 21 dm3 oil tank directly behind the engine.
The sanitary version of the pilot's cabin is open. Further in the sanitary compartment he was sick on a stretcher or in a sitting position. Cabin design in HD-14 S version from aluminum sheet, in H-28 S version from plywood. The interior of the cabin was equipped with windows on the back. The stretcher was inserted through a large doorway in the starboard side.
Wooden texture, covered with canvas.
Classic solid chassis with main front support. Double bicycle wheels with covers. Between them there are skids that prevent any possible cabotage. You can mount skis instead of wheels. There is a skid at the back.
Le Rhône C star-rotary motor with 59 kW (80 hp) nominal power. The use of a rotary engine causes the typical behavior of an aircraft with such a drive - gyroscopic effect.
Data T-T Hanriot H-28
- Span of 10.26 m,
- Length 7.25 m,
- High 2.95 m,
- Bearing area 34.0 m2.
- Curb weight 525 - 575 kg,
- Payload 255 kg
- Total weight 780-830 kg.
- Maximum speed 115 km / h,
- The climbing time per 1,000 m is 10 minutes,
- Practical ceiling of 3,200 m,
- Flight time 3 hours.
Written by Karol Placha Hetman
Kraków 2020-03-26
00124a Section 1924
CWL Mokotów, WWS „Samolot” Hanriot H-28
Poland
School and sanitary aircraft
Tally
In total, there were 295 Hanriot H-28 and derivative aircraft in Poland. 75 aircraft were built in Warsaw at CWL, and 120 aircraft at WWS "Airplane" in Poznań. Hanriot H-28 S sanitary aircraft were 18 copies.
Written by Karol Placha Hetman
